
 Northeastern University
Northeastern UniversityI am Li Chen (陈李), an undergraduate student in Software Engineering at Northeastern University, China. Since 2023, I have been conducting research in the Smart Internet Group, supervised by Prof. Yong Jiang and Prof. Qing Li. I will pursue my Ph.D. in Computer Science and Technology at Tsinghua University (SIGS) starting in 2026.
My research interests span Large Language Models (LLMs), distributed systems, and their applications, with a particular focus on interpretability and reasoning mechanisms in LLMs, as well as distributed systems for LLMs and other areas for acceleration.
Education
-
 Northeastern University, ChinaCollege of Software Engineering
Northeastern University, ChinaCollege of Software Engineering
Undergraduate StudentSep. 2022 - present
Experience
-
 Tsinghua UniversityResearch InternSep. 2023 - Apr. 2025
Tsinghua UniversityResearch InternSep. 2023 - Apr. 2025
Honors & Awards
-
Outstanding Graduate (Liaoning Province, China)2025
-
National Scholarship, China2024
-
National Scholarship, China2023
-
Outstanding Student of Northeastern University (Top 1%)2023
News
Selected Publications (view all )
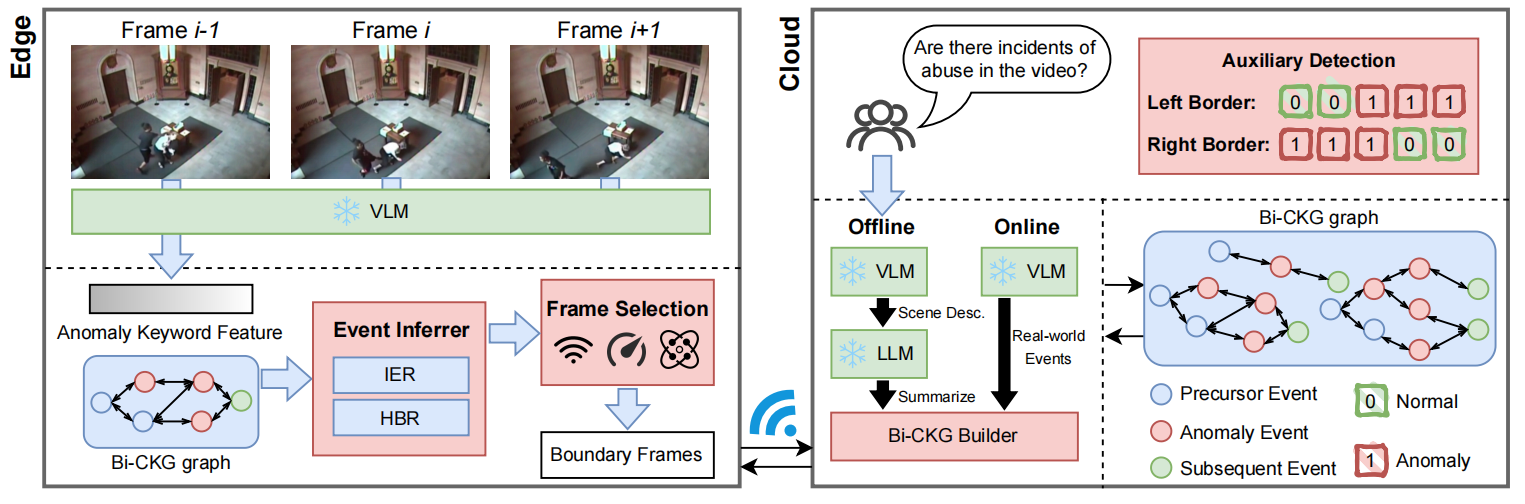
HoloTrace: LLM-based Bidirectional Causal Knowledge Graph for Edge-Cloud Video Anomaly Detection
Hanling Wang, Qing Li#, Li Chen, Haidong Kang, Fei Ma, Yong Jiang# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACMMM 2025) 2025
Video anomaly detection (VAD) is vital for public safety, yet current approaches struggle with limited generalization, low interpretability, and high resource demands. To address these challenges, we propose HoloTrace, an edge-cloud collaborative VAD system that integrates large language models (LLMs) to construct and update a novel bidirectional causal knowledge graph. At the edge, HoloTrace leverages LLM-based cross-modal understanding and employs Hidden Markov Model (HMM) for bidirectional event reasoning, obtaining anomaly boundaries with low computational overhead. On the cloud side, LLMs are leveraged to dynamically update the Bi-CKG graph with key frames sent from the edge, in order to update causal relationships between events. Additionally, we introduce SVAD, a new large-scale VAD dataset comprising 632 real-world surveillance videos across 10 anomaly types and diverse scenes, with manually labeled frame-level annotations. Experimental results demonstrate that HoloTrace not only achieves the highest accuracy but also enhances interpretability and efficiency, paving the way for more generalizable and explainable video anomaly detection systems.
HoloTrace: LLM-based Bidirectional Causal Knowledge Graph for Edge-Cloud Video Anomaly Detection
Hanling Wang, Qing Li#, Li Chen, Haidong Kang, Fei Ma, Yong Jiang# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACMMM 2025) 2025
Video anomaly detection (VAD) is vital for public safety, yet current approaches struggle with limited generalization, low interpretability, and high resource demands. To address these challenges, we propose HoloTrace, an edge-cloud collaborative VAD system that integrates large language models (LLMs) to construct and update a novel bidirectional causal knowledge graph. At the edge, HoloTrace leverages LLM-based cross-modal understanding and employs Hidden Markov Model (HMM) for bidirectional event reasoning, obtaining anomaly boundaries with low computational overhead. On the cloud side, LLMs are leveraged to dynamically update the Bi-CKG graph with key frames sent from the edge, in order to update causal relationships between events. Additionally, we introduce SVAD, a new large-scale VAD dataset comprising 632 real-world surveillance videos across 10 anomaly types and diverse scenes, with manually labeled frame-level annotations. Experimental results demonstrate that HoloTrace not only achieves the highest accuracy but also enhances interpretability and efficiency, paving the way for more generalizable and explainable video anomaly detection systems.